1. What is LINUX?
Linux is an open-source operating system founded by Linus Torvalds. An operating system is software that directly manages a system’s hardware and resources, like CPU, memory, and storage. It was completely written from scratch. It is light in weight.
Linux OS --> Linux Kernel + GNU

Flavour's of Linux:
Ubuntu
Red hat
CentOS
Kali Linux
Fedora
Debian
2. Features of Linux?
Open-Source
Multiuser --> Multitasking
Secure and light in weight
Simplified Updates for all Installed Software
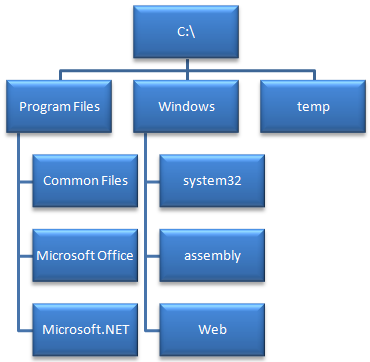
3. File System Hierarchy of Windows vs Linux:
Windows FSH:
Linux FSH:
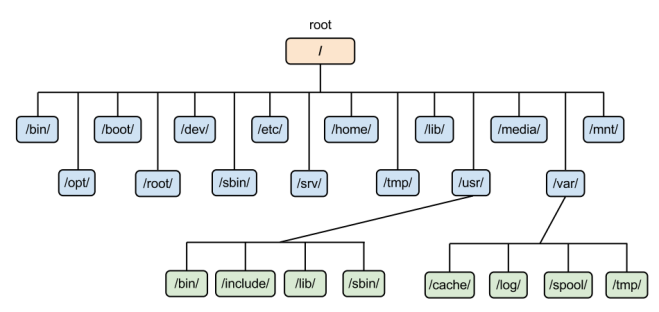
1. /root: In Linux, everything starts from the root (/). This is the starting point of FSH. It is the home directory for the root user (superuser).
2. /bin: Essential command binaries that need to be available in single-user mode; for all users, e.g., cat, ls, cp.
3. /boot: Boot loader files, e.g., kernels, initrd
/dev: Essential device files, e.g., /dev/null. These include terminal devices, USB, or any device attached to the system.
/etc: Host-specific system-wide configuration files. Contains configuration files required by all programs.
6. /home: Users’ home directories, containing saved files, personal settings, etc. Home directories for all users to store their files.
7. /lib: Libraries essential for the binaries in /bin/ and /sbin/. Library filenames are either ld* or lib*.so.*
- /media: Mount points for removable media such as CD-ROMs (appeared in FHS-2.3). Temporary mount directory for removable devices.
9. /mnt: Temporarily mounted filesystems. Temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount filesystems.
10. /opt : Optional application software packages. Contains add-on applications from individual vendors. Add-on applications should be installed under either /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
11. /sbin : Just like /bin, /sbin also contains binary executables. The Linux commands located under this directory are used typically by the system administrator, for system maintenance purposes. Example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon.
12. /var: Variable files. The variable data files such as log files are located in the /var directory.
13. /tmp: Temporary Files. It's a directory that contains temporary files created by the system and users.
4. Linux Basic Commands:
pwd -> it shows the present working directory

ls -> it shows available files and directory list in the present working directory

ls -la -> contains list of folders/files with all details and permissions of users/groups/others

uname -> it shows the name of the kernel

uname -r -> it shows a version of the kernel

cd -> to change the directory

clear-> use to clear screen
whoami ->currently login user

history -> it shows the list of previously used commands

date -> current date and time

Create a file or directory
To Create a single directory
-> mkdir devops

To Create multiple directories
-> mkdir qa prod test

Directory path(directory inside the directory)
->mkdir -p /production/qa/prod/test/devops


To create several directories
-> mkdir /react{1..10}

Create File:p
Touch: The touch command is used to create an empty file, we can’t write data in a file, can’t edit or save a file.
To create a single file
->touch notes

To create multiple files
->touch python java c#

To create several files
->touch books{1..10}

For Copy and paste
cp: It is used to copy and paste files or directory
Syntax: cp <option> <source> <destination>
Options:
-r for recursive
-v for verbose
-f for forcefully
For copy file
->cp hello.txt prod

->cp -rvf devops/hello.txt /home
To copy all data which start from the D alphabet
->cp -rvf /root/D* /home
To remove files and directory
->rm -rvf /devops/c#


For moving or renaming files and directory
->mv /home/dev /root/Desktop
For renaming files or directory
->mv dev devops

For Hiding a file
-> To hide a file just put a dot( . ) before file name. And to view it write (ls -la)


#
