1. What is DevOps?
DevOps is a combination of software development (dev) and operations (ops). It is defined as a software engineering methodology that aims to integrate the work of development teams and operations teams by facilitating a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility.
DevOps "Dev =development” and "Ops=operations" is the combination of practices and tools designed to increase an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services faster than traditional software development processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
2. What are Automation, Scaling, and Infrastructure?
DevOps automation is the addition of technology that performs tasks with reduced human assistance to processes that facilitate feedback loops between operations and development teams so that iterative updates can be deployed faster to applications in production.
There are various automation tools for DevOps, few of them are:
Jenkins
Git and GitHub
Docker
Kubernetes
Ansible
Terraform
Scaling is another important aspect of DevOps. As applications grow and more users interact with them, the infrastructure supporting their needs to be able to scale up to handle the increased load. This can be achieved through the use of cloud computing resources, such as auto-scaling groups, load balancers, and distributed databases. DevOps teams need to design their applications and infrastructure to be scalable from the outset.
Infrastructure refers to the underlying technology that supports an application or service. In the context of DevOps, infrastructure can include servers, databases, networks, and other components. DevOps teams need to be able to manage their infrastructure in an automated and scalable way to support the demands of their applications. Infrastructure as code (IaC) is a common practice in DevOps, where infrastructure is defined and managed using code, which enables teams to automate the management of their infrastructure.
3. Why DevOps is important?
Maximizes Efficiency with Automation.
Reduced Deployment Rollbacks, failures, and Time to Recover.
Increased reliability and improved collaboration.
Enhanced Scalability.
Cost Saving.
4. How is DevOps different from agile methodology?
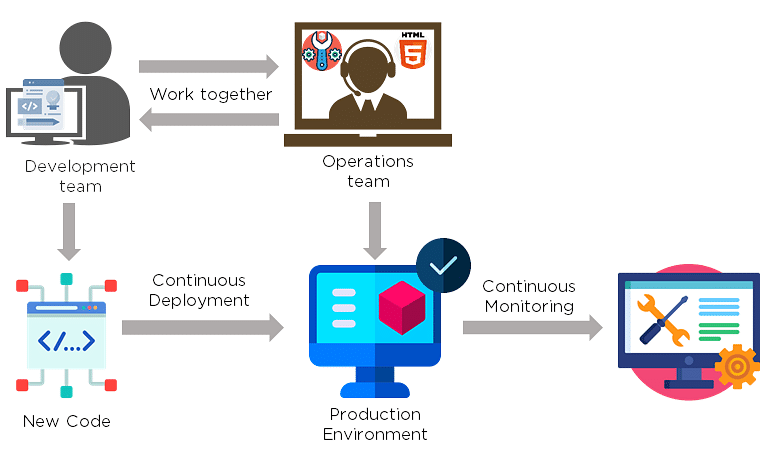
DevOps is a culture that allows the development and the operations team to work together. This results in continuous development, testing, integration, deployment, and monitoring of the software throughout the lifecycle.
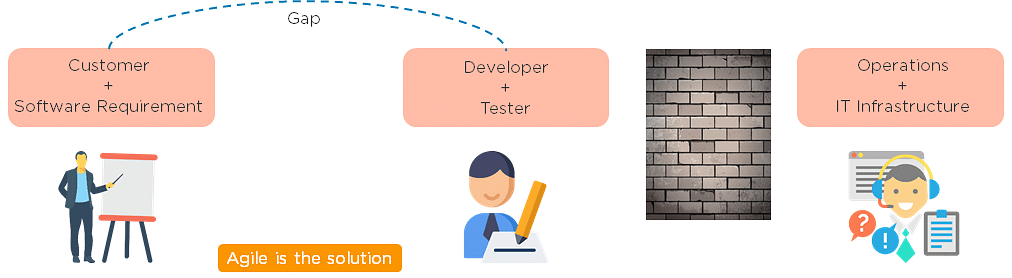
Agile is a software development methodology that focuses on iterative, incremental, small, and rapid releases of software, along with customer feedback. It addresses gaps and conflicts between the customer and developers.
5. What are the different phases in DevOps?
The various phases of the DevOps lifecycle are as follows:
Plan: Initially, there should be a plan for the type of application that needs to be developed. Getting a rough picture of the development process is always a good idea.
Code: The application is coded as per the end-user requirements.
Build: Build the application by integrating various codes formed in the previous steps.
Test: This is the most crucial step of application development. Test the application and rebuild, if necessary.
Integrate: Multiple codes from different programmers are integrated into one.
Deploy: Code is deployed into a cloud environment for further usage. It is ensured that any new changes do not affect the functioning of a high-traffic website.
Operate: Operations are performed on the code if required.
Monitor: Application performance is monitored. Changes are made to meet the end-user requirements.

